Are you encountering the “Permission Denied” error while working with PHP8-FPM on your Ubuntu Linux system? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! This is a common issue that many developers and system administrators face. In this guide, we’ll walk through how to fix this error to ensure your PHP application runs smoothly.
Impact of the “Permission Denied” Error
The “Permission Denied” error can manifest in various ways, causing interruptions in your workflow:
✅ File uploads: You may be unable to upload files to the server.
✅ File modifications: Editing files might become impossible.
✅ Code execution: PHP scripts may not run or display correctly.
✅ Code deployment: You might be blocked when deploying code or accessing cached data.
Important Note: When I first started managing servers, I once used
chmod 777to quickly “fix” permission issues. However, I soon realized that this was a major security risk. Don’t repeat my mistake!
Set Proper Ownership (USER) to Fix “Permission Denied”
After installing PHP on Ubuntu, you need to adjust some settings to resolve this error. Follow these steps:
1. Back Up the Configuration File
Before making any changes, create a backup so you can restore it if needed. (I’ll demonstrate this using PHP 8.3):
sudo cp -R /etc/php/8.3/fpm/pool.d/www.conf /etc/php/8.0/fpm/pool.d/www.conf.bak
sudo nano /etc/php/8.3/fpm/pool.d/www.conf2. Edit the www.conf File
Open the PHP-FPM pool configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/php/8.3/fpm/pool.d/www.confInside this file, locate the [www] section. This section defines the user and group under which PHP-FPM processes will run. By default, they are set to www-data:
user = www-data
group = www-dataOn Ubuntu, when using Nginx or Apache, web projects are typically stored in /var/www/. Running PHP-FPM with the www-data user may lead to the “Permission Denied” error if your user account lacks access to these files.
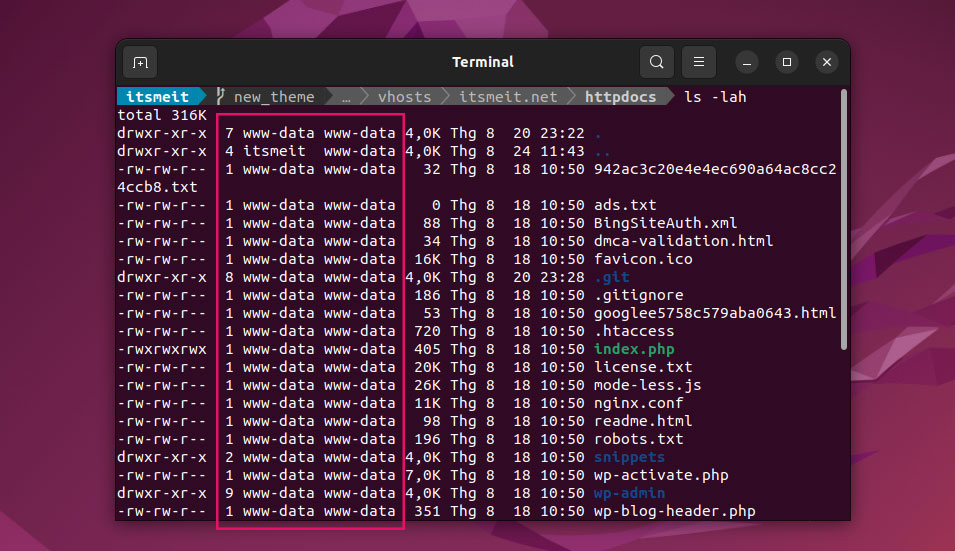
3. Change File Ownership
The solution is to grant proper permissions to the user you’re using on the system. In this example, we assign permissions to the user “itsmeit” (replace it with your actual username).
user = itsmeit
group = www-data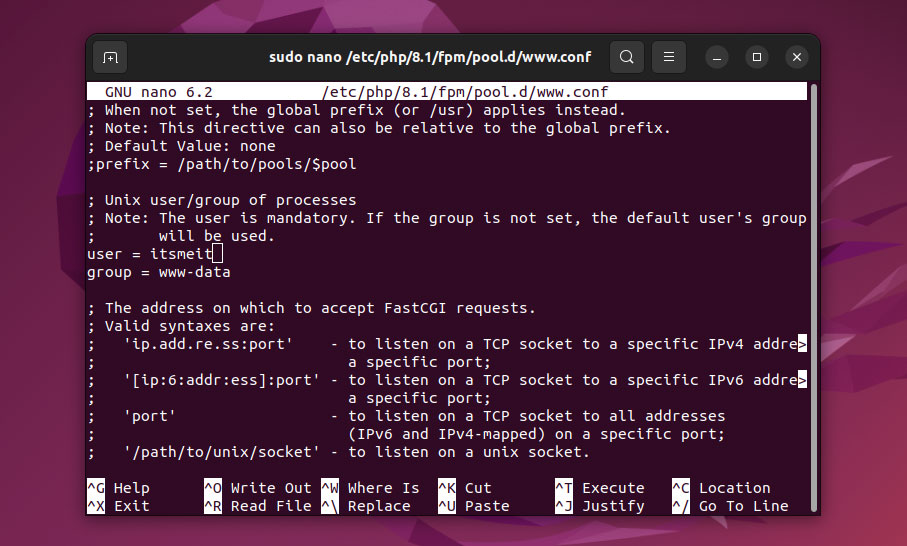
After making changes, restart PHP-FPM to apply them:
sudo service php8.3-fpm restart4. Update Project Directory Ownership
Once access permissions are granted, update the project directory’s ownership to ensure your user has full control over files and directories within the project:
sudo chown -R itsmeit:www-data /var/www/your_project_directorImportant Notes:
🔹 Replace "itsmeit" with your actual username.
🔹 Replace "your_project_directory" with the actual path to your project directory.
🔹 The -R (recursive) flag ensures that ownership is changed for all files and subdirectories within the project.
🔹 The www-data group is commonly used by web servers, so keeping this group ensures that your server can still access and serve your files properly.
Fixing the “Permission Denied” error is just one step in optimizing PHP8-FPM on Ubuntu. As you continue developing and deploying PHP applications, you’ll discover many other useful configurations and optimizations. I believe that with persistence and experimentation, your system will become more stable and secure.
Don’t be afraid to explore – I’ve been through this stage too!