Why Optimize MySQL?
MySQL is one of the most widely used database management systems, commonly used in web applications like WordPress, Laravel, and Magento. Without optimization, MySQL can become a “bottleneck,” causing significant performance degradation across your system. Optimization helps:
- Speed up query processing.
- Reduce CPU and RAM load.
- Improve the scalability of websites or applications.
Setting Up an Optimized MySQL on Linux VPS
1. VPS Sample Configuration
- CPU: 2 cores.
- RAM: 4GB.
- Storage: SSD NVMe.
- Database: MariaDB or MySQL (you can apply similar steps for either).
2. Sample MySQL Configuration
First, to identify which file is configuring MySQL, run the following command:
mysqld --help --verbose | head -n13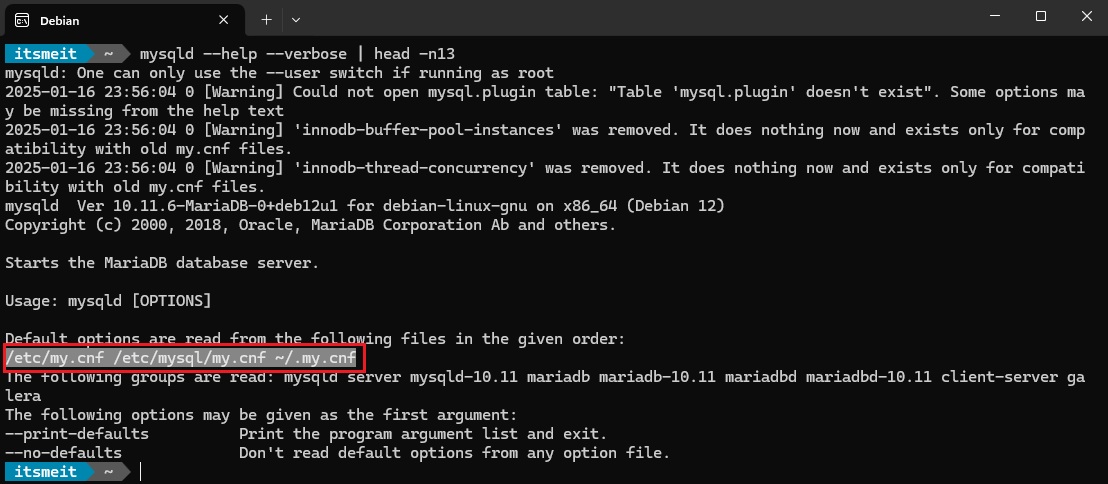
From the output, you can see the configuration files in the order /etc/my.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf ~/.my.cnf. You can make adjustments in any of these files.
For this example, I’ve copied the entire sample MySQL configuration into /etc/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf.
Restart MySQL to Apply Changes:
sudo service mysql restartExplanation of Configurations:
- innodb_buffer_pool_size: RAM dedicated to InnoDB database, around 50-70% of physical RAM.
- tmp_table_size & max_heap_table_size: Limits on temporary table size, reducing disk writes.
- query_cache_size & query_cache_type: Disable query cache to avoid locking issues on modern systems.
Install and Use MySQLTuner
MySQLTuner is a tool that analyzes MySQL configuration and provides specific recommendations based on the current database state, helping you fine-tune for optimal performance.
Source: https://github.com/major/MySQLTuner-perl
1. Install MySQLTuner
Download and install MySQLTuner using the following commands:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/major/MySQLTuner-perl/master/mysqltuner.pl
chmod +x mysqltuner.pl2. Run MySQLTuner:
Once installed, execute MySQLTuner:
./mysqltuner.plExample output screenshot:
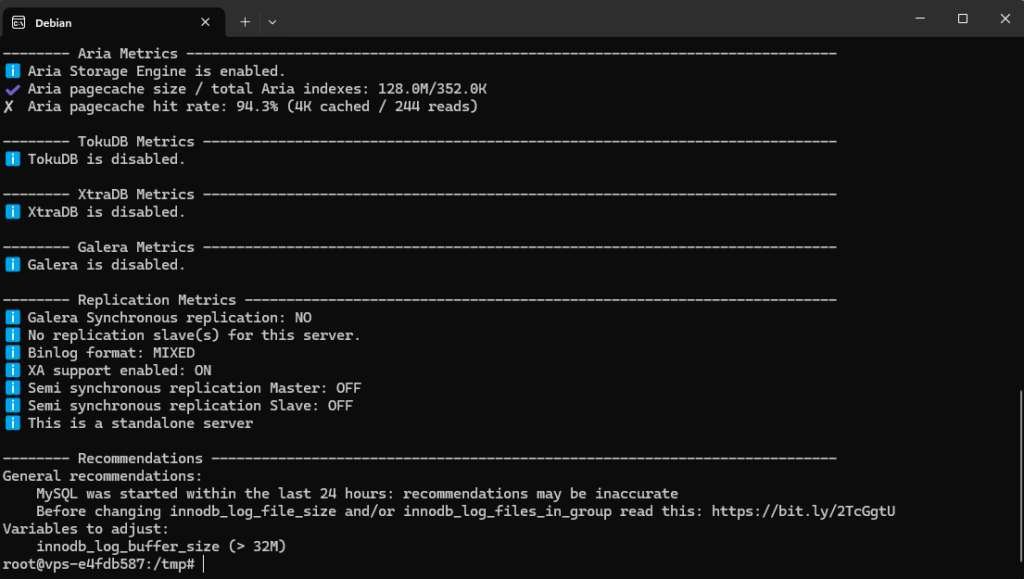
Applying MySQLTuner Recommendations
1. Analyze and Apply Recommendations:
Based on the report from MySQLTuner, I made the following adjustments:
- Increase InnoDB log buffer:
innodb_log_buffer_size = 32M- Increase temporary table size:
tmp_table_size = 128M
max_heap_table_size = 128MNote: Refer to the MySQLTuner suggestions displayed in your terminal to make the necessary configuration adjustments.
2. Restart MySQL
After making changes, restart MySQL:
sudo service mysql restartCheck Effectiveness After Optimization
Re-run MySQLTuner to test applied changes:
./mysqltuner.plLook for Improvements:
- Reduced
Temporary tables on disk. - Improved InnoDB Read/Write performance.
Tips:
- Run MySQLTuner regularly (every 24-48 hours, depending on traffic).
- Pay attention to MySQLTuner’s analysis results during each test to assess real-world performance.
- Don’t blindly apply all recommendations—understand the meaning behind each setting before changing it.
- Monitor logs to detect issues early and address them promptly.
Optimizing MySQL isn’t just about changing configurations—it’s a continuous process of testing and adjustment. Use MySQLTuner as a powerful tool to analyze and implement appropriate improvements. You can refer to the official MySQL/MariaDB documentation for a deeper understanding of configuration options. If you have any questions or want to share your experiences, feel free to leave a comment below!
References: #innodb_log_buffer_size