Botnet attacks are on the rise, with many users recently discovering their computers infected after installing software from untrusted sources. This can lead to serious consequences, including the loss of personal data. This article will help you identify signs of a botnet infection and provide effective prevention and removal methods to safeguard your system.
What are botnet? Types of attacks and purposes?
A botnet (short for “robot network”) is a collection of devices connected to the Internet, each device running one or more computer programs called “bots”. Botnet are capable of performing many actions such as distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, stealing data, sending spam, and allowing attackers to access device information. Without botnet containment, the botnet owner can control the entire fleet of devices using command and control software. The term “botnet” is formed from combining “robot” and “cyber,” which often has negative or malicious connotations when used.

When your computer is infected and becomes part of a botnet, it performs malicious activities determined by the attacker, including cyberattacks, spamming, DDoS attacks, information theft, etc. personal information and other illegal acts. Computers in a botnet often operate without the user’s awareness, leaving computer owners unaware that they are engaging in malicious activities.
Types of attacks and purposes of botnet include:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack: Botnet can be used to generate a large number of requests to a website or service, causing it to become overloaded and inoperable. The purpose of a DDoS attack is to disrupt the target’s online activity.
- Data theft: Botnet can be used to infect computers or devices, then steal important information such as bank accounts, personal information, credit card information and important data other.
- Spam: Botnet can be used to send mass spam messages to millions of people, jamming inboxes and hindering the transmission of valid information.
- Unauthorized connections: An attacker can use botnet to gain unauthorized access to computers or devices, and then use them as a starting point for other attack activities or to access data.
- Drilling for profit: Botnet can also be used to mine the resources of infected computers or devices, for example, mining processing power to mine cryptocurrencies (coin mining) without permission. owner’s permission.
How to Check for Botnet Infections on Your Computer
Some methods for testing a computer for botnets or malware require a background in cybersecurity. However, here are some fundamental steps you can take to detect signs of a botnet on your computer and take measures to remove it and prevent botnet attacks.
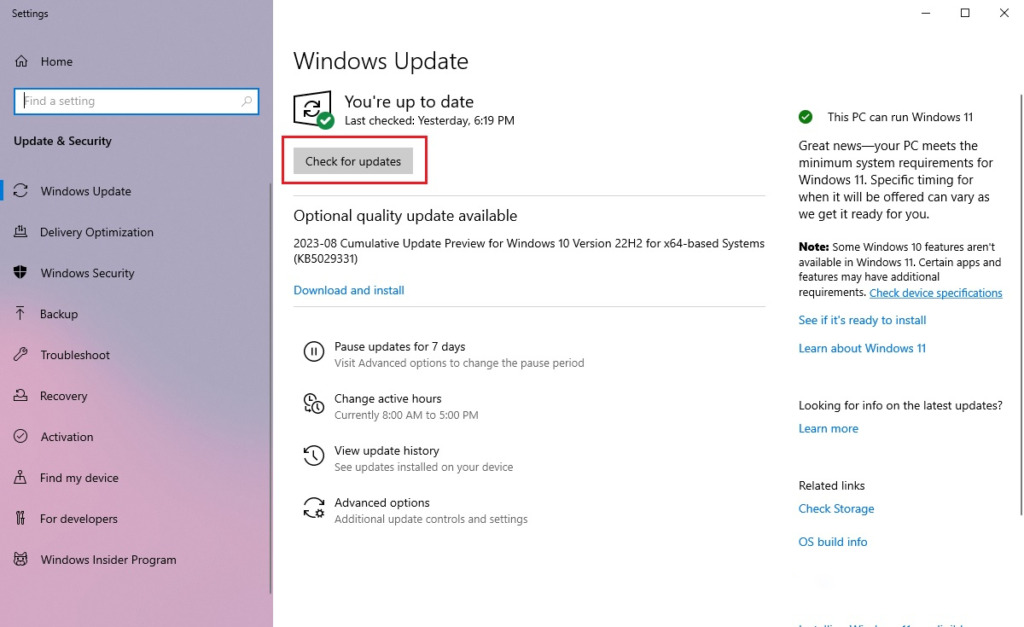
Update software and operating system:
Make sure your computer’s operating system and security software are up to date. This helps close security holes that malicious actors can use to get into the system.
Scanning for Malware to Remove Botnet:
Use anti-malware software or an anti-virus application to scan your entire computer system and remove botnet. Make sure the software is up to date and perform a thorough scan to detect all types of malware, including botnet.
First enable the “Windows Defender” function, which is the default protection function of Windows. You can open it by going to “Settings -> Windows Security -> Open Windows Security”.
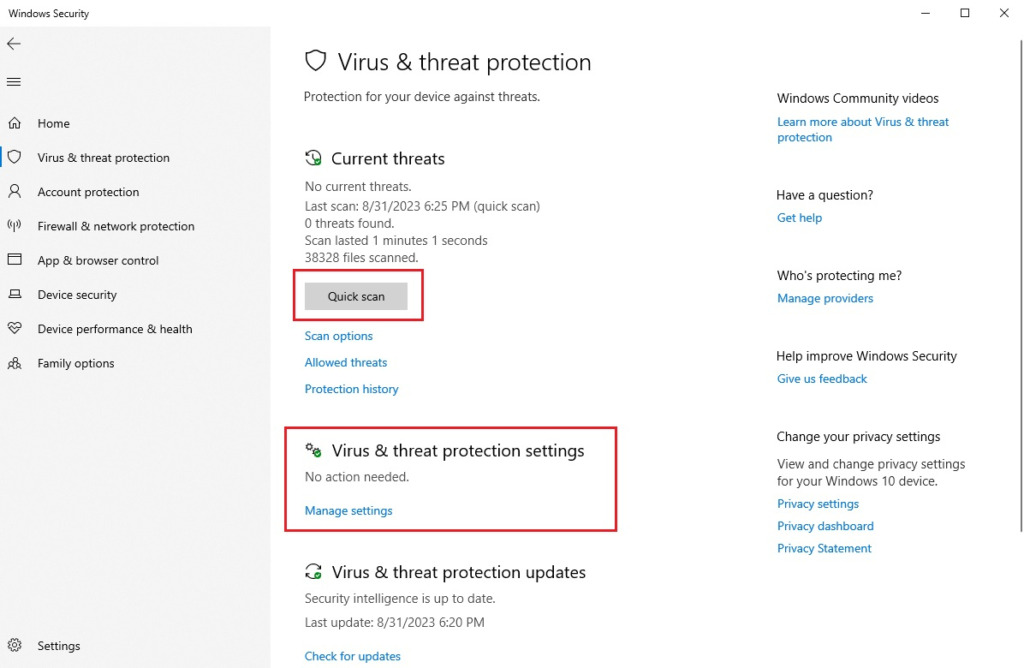
Continue to click on “Manage settings” and enable all Windows protection functions.
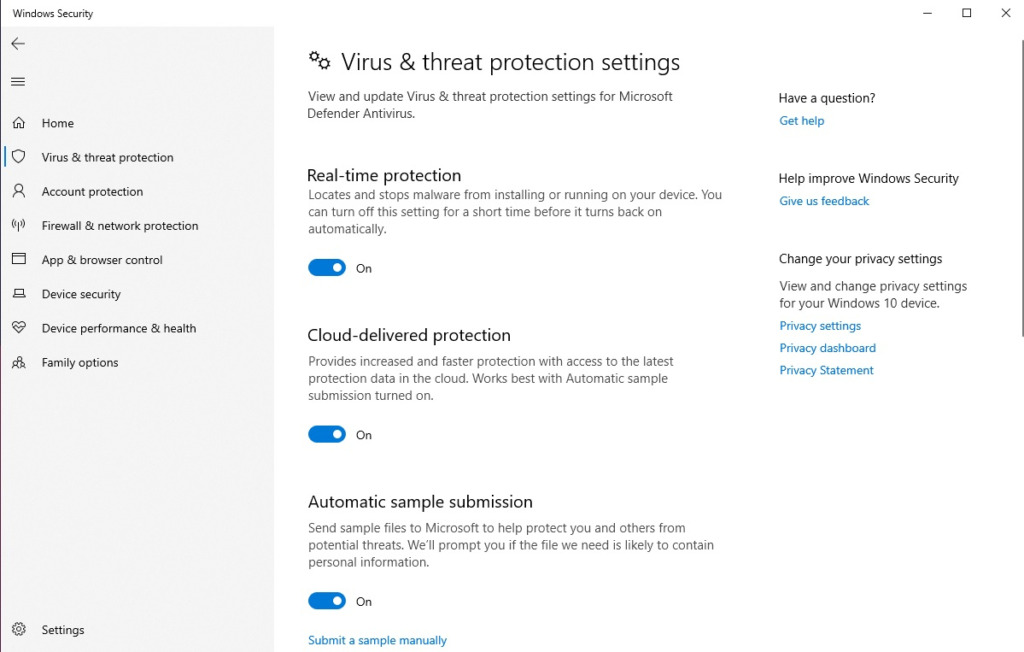
After you have enabled the “Windows Defender” computer protection function, then click “Scan” to check for viruses and security holes, it will also help you prevent threats, prevent botnet attacks.
Check performance and resource consumption:
Botnet often consume computer resources , causing slow or unusual performance. Check if your computer has unusual performance, slows down, or uses more CPU and memory than usual. How to check is as follows:
Find and open “Tast mannager” in the Windows search bar. Here you will see running applications and display RAM and CPU consumption on the system.
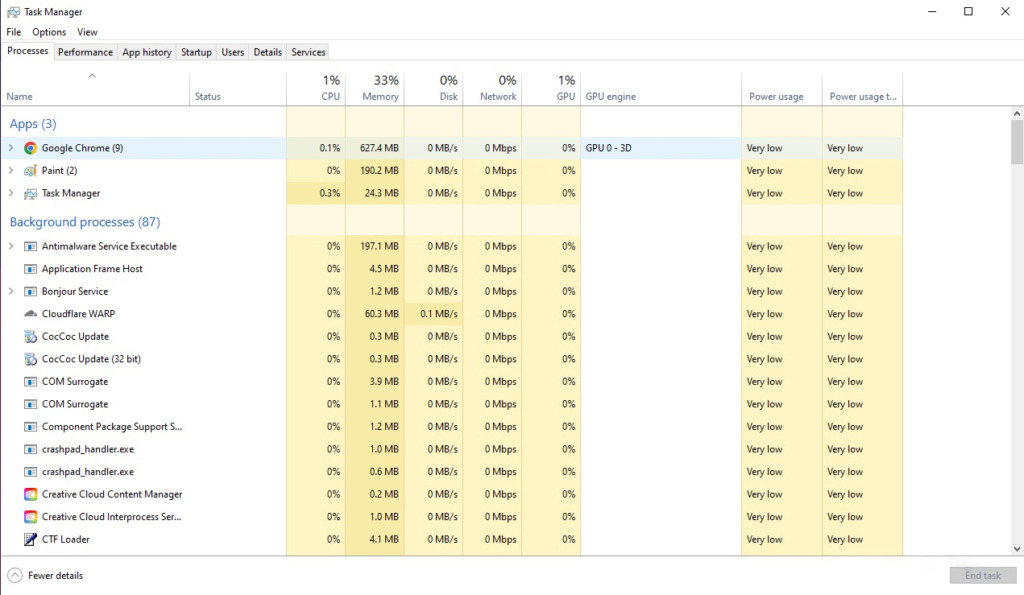
The tabs in “Task Manager” have the following functions:
- Processes: Displays a list of processes running on the computer, including the name of the process, the system resources the process is using, and the user name corresponding to each process. Through these processes you can also control, remove and prevent botnet attacks.
- Performance: Displays information about system resource usage such as CPU, memory, and disk. This helps you monitor overall system activity and determine whether an issue is affecting performance.
- App history: Displays information about resource usage by applications over a specific period of time. You can see how much CPU, memory and data has been used by applications.
- Startup (Start with system): Displays a list of applications and programs configured to start with the system. You can manage these applications to speed up the computer startup.
- Users: Displays a list of users currently logged on to the computer and the number of processes each user is running.
- Details: Displays a detailed list of running processes, including process ID, corresponding user, and used resources. Thereby you can detect suspected malicious software and prevent botnet attacks.
- Services: Displays a list of system services and their status (running, down). You can manage these services from here.
- Performance Monitor: Opens a window containing detailed charts and parameters about real-time system resource usage.
These tabs in “Task Manager” help you monitor and manage processes and resources on your computer, thereby helping you identify performance problems or disruptive, unsafe applications.
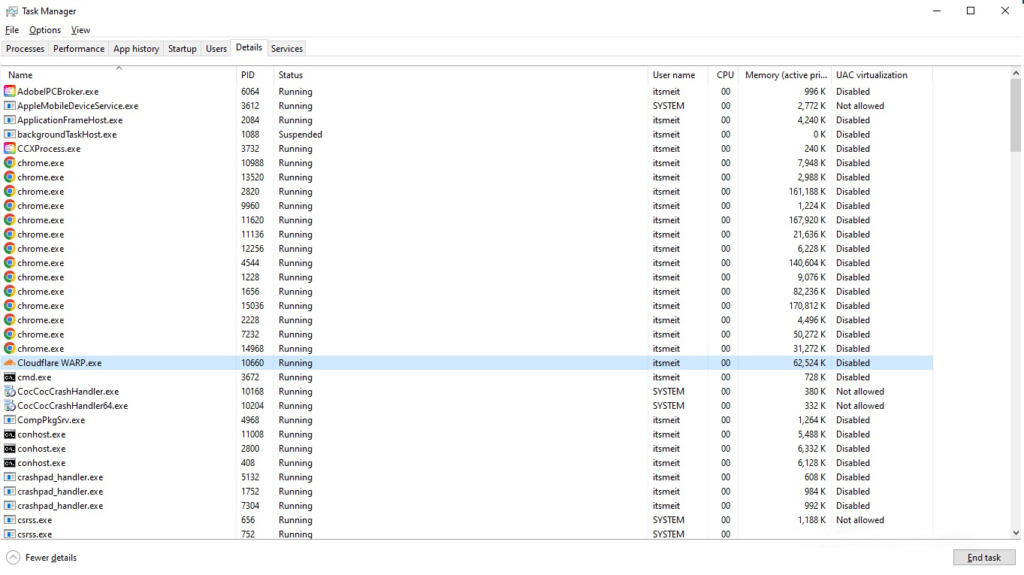
Check network traffic:
Checking network traffic is an important method to determine whether botnet activity is taking place on your computer. Here are some detailed steps to examine network traffic and detect signs of botnet activity:
- Use network monitoring tools: There are many network monitoring tools that can help you monitor network traffic on your computer, prevent botnet attacks. Some popular tools include Wireshark, GlassWire, and NetWorx. Install and configure this tool to monitor data passing through your computer.
- Identify uncommon connections: Use a network monitoring tool to review the list of active network connections on your computer. Search for unfamiliar IP addresses or domain names, especially those located in countries unrelated to your normal activities.
- Check traffic for unusual ports: Botnet often use unusual ports to communicate with remote controllers. Use a network monitoring tool to review traffic for ports that are not frequently used for network communication, such as port 6667 (IRC) or port 31337 (Backdoor).
- Encrypted Traffic Tracking: Some botnets use encryption to conceal their activity. However, inspecting encrypted traffic can be time-consuming and requires specialized knowledge. If you detect suspicious encrypted traffic, you should consult a security professional for assistance in prevent botnet attacks.
- Compare with regular data: Master your computer’s regular network traffic data to compare with current traffic. Sudden and unexplained differences in network traffic can be a sign of botnet activity.
If you detect any suspicious signs in network traffic, such as unusual usage patterns, access from unfamiliar IP addresses, or any other anomalies, you can take measures to mitigate the threats and prevent botnet attacks.
Use an anti-botnet tool:
There are several specialized tools to check and remove botnet from computers such as: McAfee Stinger, Norton Power Eraser, Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool or Malwarebytes Anti-Malware .
In this tutorial we will use “ Malwarebytes Anti-Malware ”, which is a popular anti-malware tool with the ability to detect and remove all types of malware, including botnet. This tool offers a free version and a paid version with extended features.
How to install and use Malwarebytes Anti-Malware:
– Step 1: Visit the website www.malwarebytes.com , you can pay to buy the Premium version with extended features, or download the free version.
– Step 2: Click on the file “MBSetup.exe” and “Next” until “Finish”.
– Step 3: The interface of Malwarebytes software is user-friendly. Click “Scan” to initiate the virus scanning process. If you detect an infected file or suspect it might be a botnet or virus, you can search for the file’s name on Google to gather information about it. Then, you can take appropriate actions to address the issue as needed.
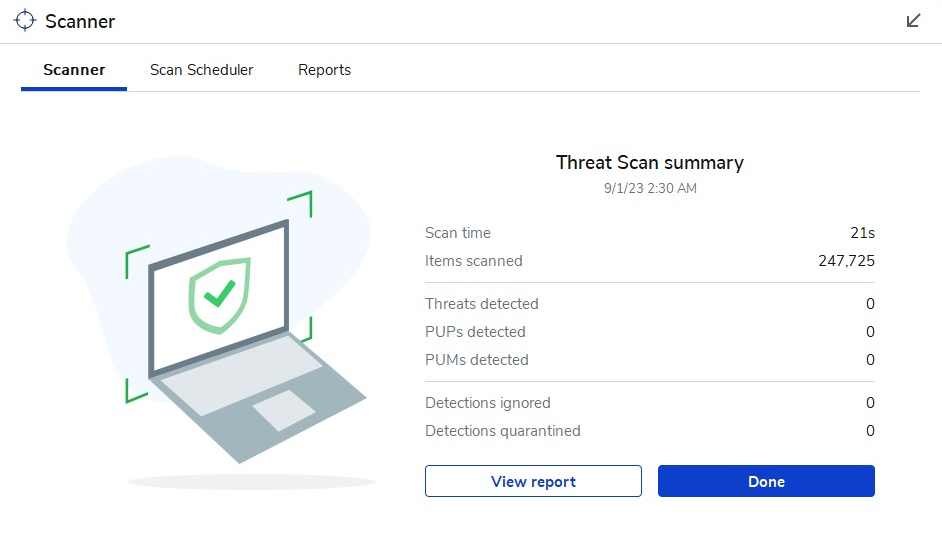
Of course, in addition to Malwarebytes , you can also try with other similar software.
Prevent Computer Infections from Viruses and Botnet Malware
Keeping Up-to-Date with Technology Knowledge
To prevent or remove botnets, it’s important to first educate yourself and stay updated about technology, the internet, and various forms of fraud. For instance, when someone sends you a link, make sure you have enough information about it before clicking on it. These links often impersonate banks or companies, or they may contain harmful virus files.
Disable Browser Cookies to Enhance Privacy
A cookie is a small form of data that is stored on a user’s computer when they visit a website. Cookies often contain information about users’ browsing behavior, provide personalized services, and help websites remember information about users when they return. Cookies are used to provide a better browsing experience, such as storing login information, shopping carts, browsing history, and other personal settings.
However, cookies also have disadvantages and can pose security and privacy issues. Moreover, cookies are frequently employed to maintain user sessions on websites. Nonetheless, if you don’t protect against botnets, cookies can potentially provide attackers with an opportunity to utilize botnets to compromise user accounts without needing the password, and even without undergoing security authentication.
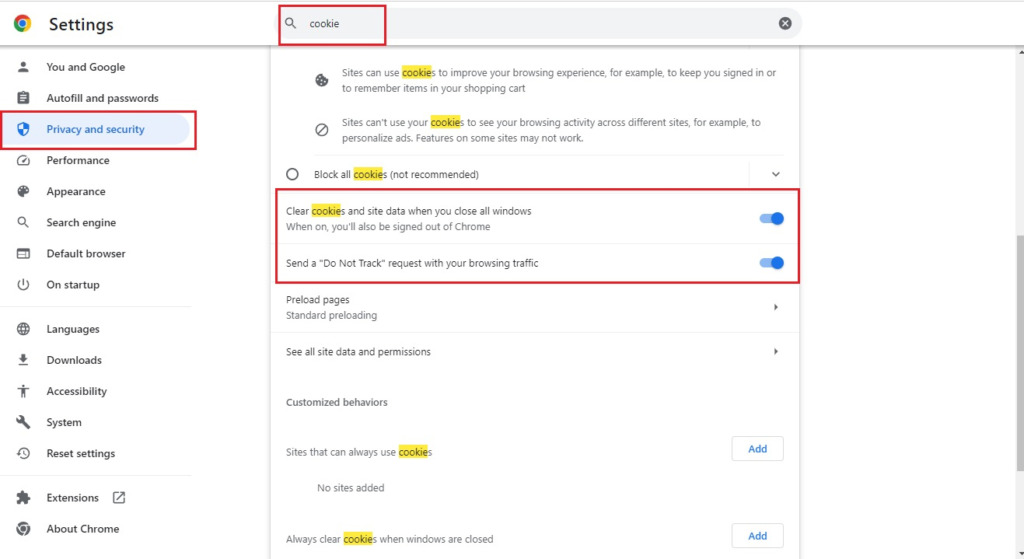
If you want to ensure safety, you can set off cookie saving on your browser, for example Chrome, you can go to settings, find “cookies” and enable the function to delete cookies when closing the browser. This is a basic but also very safe way to prevent botnet attacks.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for social media accounts
All social networking accounts, including Facebook, Google, Zalo, and bank accounts, offer two-factor authentication. You can install and enable this feature to safeguard your account and prevent prevent botnet attacks. Additionally, remember to change your password regularly for increased security. Importantly, avoid saving personal information, bank account details, or credit card information in your browser.

We aim to share knowledge with you to enhance your understanding of phishing scams and how to prevent your computer from being infected with malicious code, thereby preventing botnet attacks. We hope this information will educate and motivate you to stay updated in order to protect yourself from online risks.